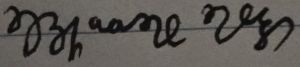Kiryattic: Difference between revisions
(→Verbs) |
(→Verbs) |
||
| Line 536: | Line 536: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! colspan=2 rowspan=2 | | ! colspan=2 rowspan=2 | | ||
! colspan=2 | | ! colspan=2 | Past optative | ||
! colspan=2 rowspan=2 | | ! colspan=2 rowspan=2 | | ||
! colspan=2 | | ! colspan=2 | Past potential | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Positive | ! Positive | ||
Revision as of 18:59, 11 January 2026
| Kiryattic κιρϊάάκϊάν κιάλε | |
|---|---|
| Pronounced: | /kir.jæː.kjæ̃ kiæ̯.le/ [ˈkir.jæː.ˌcɛ̃ ˈcæ.le] |
| Species: | Human |
| Spoken: | Greece |
| Writing system: | Greek |
| Genealogy: | Proto-Uralic
|
| Typology | |
| Morphological type: | Agglutinative |
| Morphosyntactic alignment: | Nominative |
| Basic word order: | Free |
| Credits | |
| Creator: | Lumi |
| Created: | January 5th, 2026 |
Kiryaakattic is a Finnic language spoken in Greece. It, as with most Finnic languages, remains decently conservative. Kiryaakattic is most distinguishable by the preservation of word final Proto-Finnic *k (as modern /g/) and *h (as modern /k/).
Phonology
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | |
| Plosive¹ | p, b | t, d | c, ɟ | k, g |
| Fricative | s | ç | x | |
| Approximant | w | r, l | j |
- 1: Aspirated voiceless plosives exist in Greek loanwords
| Neutral¹ | Front | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High | i | y | u |
| Mid-High | e | ø | o |
| Mid-Low | œ | ɔ | |
| Low | æ | ɑ |
| Neutral¹ | Front | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High | ĩ | ỹ | ũ |
| Mid | ẽ | ø̃ | õ |
| Low | ɛ̃ | ɑ̃ |
- 1: Vowels unaffected by harmony
- 2: All vowels can be long
Orthography
| Letter | Transcription | Name | Pronunciation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finnic | Greek | |||
| α | a | αλφα | /ɑ/ | |
| ά | ä | á | άικά | /æ~a/ |
| β | b | βετα | /b/ | |
| γ | g | γαμμα | /g/ | |
| δ | d | δελτα | /d/ | |
| ε | e | επσιλον | /e/ | |
| ζ | z | ζετα | /(d)z/ | |
| θ | th | θετα | /θ/ | |
| ι | i | ιωτα | /i/ | |
| ϊ | j | ï | /j/ | |
| κ | k | καππα | /k/ | |
| λ | l | λαμδα | /l/ | |
| μ | m | μυ | /m/ | |
| ν | n | νυ | /n/ | |
| ο | o | ομικρον | /o/ | |
| ό | ö | ó | /ø/ | |
| π | p | πι | /p/ | |
| ρ | r | ρο | /r/ | |
| σ | s | σιγμα | /s/ | |
| τ | t | ταυ | /t/ | |
| υ | u | υπσιλον | /u/ | |
| ύ | ü~y | ú | /y/ | |
| ϋ | w | ü | /w/ | |
| φ | ph~f | φι | /f/ | |
| χ | h | χι | /x/ | |
| ω | å | ō | ωμεγα | /ɔ/ |
| ώ | ô | ṓ | /œ/ | |
It is important to note that handwritten Kiryaakattic often looks nothing like its displayed counterpart, as handwritten Kiryaakattic uses many unique letter forms, and also makes extensive use of ligatures and shorthand symbols, some of which are for Greek words, rather than native ones, as with the symbol for "και" often being used in place of native "ϊα"
Grammar
Morphology
Nouns
Adjectives
Pronouns
Verbs
Verbs are highly complex, but similar to Finnish.
| Present Indicative | Present Conditional | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | ||||
| singular | 1st | λόύτάν | λόύτάκεν | singular | 1st | λόύτάδιν | λόύτάδικεν |
| 2nd | λόύτάτ | λόύτάκετ | 2nd | λόύτάδιτ | λόύτάδικετ | ||
| 3rd | λόυτάβι | λόύτάκεβι | 3rd | λόύτάδι | λόύτάδικε | ||
| plural | 1st | λόύτάνά | λόύτάκενά | plural | 1st | λόύτάδινά | λόύτάδικενά |
| 2nd | λόύτάτά | λόύτάκετά | 2nd | λόύτάδιτά | λόύτάδικετά | ||
| 3rd | λόυτάβιά | λόύτάκεβιά | 3rd | λόύτάδιά | λόύτάδικεά | ||
| passive | λόύτάδεν | λόύτάδδάγ | passive | λόύτάάδιεν | λόύτάάδιγ | ||
| Past Indicative | Past Conditional | ||||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | ||||
| singular | 1st | λόύτιεν | λόύτιεκεν | singular | 1st | λόύτιεδιν | λόύτιεδικεν |
| 2nd | λόύτιετ | λόύτιεκετ | 2nd | λόύτιεδιτ | λόύτιεδικετ | ||
| 3rd | λόυτιεβι | λόύτιεκεβι | 3rd | λόύτιεδι | λόύτιεδικε | ||
| plural | 1st | λόύτιενά | λόύτιεκενά | plural | 1st | λόύτιεδινά | λόύτιεδικενά |
| 2nd | λόύτιετά | λόύτιεκετά | 2nd | λόύτιεδιτά | λόύτιεδικετά | ||
| 3rd | λόυτιεβιά | λόύτιεκεβιά | 3rd | λόύτιεδιά | λόύτιεδικεά | ||
| passive | λόύτιεδεν | λόύτιεδδάγ | passive | λόύτιεδιεν | λόύτιεδιγ | ||
| Imperative | Potential | ||||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | ||||
| singular | 1st | — | singular | 1st | λόύτάνεν | λόύτάνκεν | |
| 2nd | λόύτάάγ | λόύτάάκάλάγ | 2nd | λόύτάνετ | λόύτάνκετ | ||
| 3rd | λόύτάάσεν | λόύτάάκάλάσεν | 3rd | λόύτάνε | λόύτάνκε | ||
| plural | 1st | λόύτάάτεμά | λόύτάάκάλάμά | plural | 1st | λόύτάνενά | λόύτάνκενά |
| 2nd | λόύτάάκά | λόύτάάκάλάκά | 2nd | λόύτάνετά | λόύτάνκετά | ||
| 3rd | λόύτάάσενά | λόύτάάκάλάσενά | 3rd | λόύτάνεά | λόύτάνκεά | ||
| Passive | λόύτάάκάεν | λόύτάάγ | Passive | λόύτάάνεεν | λόύτάάνγ | ||
| Optative | Non-finite | ||||||
| Positive | Negative | Active | Passive | ||||
| singular | 1st | λόύτάόν | λόύτάόκεν | Participle | Present | λόύτάβά | λόύτάάπά |
| 2nd | λόύτάότ | λόύτάόκετ | Past | λόύτάνύτ | λόύτάύ | ||
| 3rd | λόύτάό | λόύτάόκε | |||||
| Plural | 1st | λόύτάόνά | λόύτάόκενά | Infinitive | λόύτάάγ | ||
| 2nd | λόύτάότά | λόύτάόκετά | Gerund | λόύτάμά | |||
| 3rd | λόύτάόά | λόύτάόκεά | Action noun | λόύτάμινεν | |||
| Passive | λόύτάάκόεν | λόύτάόγ | |||||
As can be seen, Kiryaakattic has unique negative forms, these developed from the suffixation of Proto-Finnic *e- (negative verb) to the connegative form, these connegative forms were later lost, leaving only the negative forms.
In informal speech, a past potential and past optative may be heard, taking the root "-α-" and making it "-ιε-" in the potential, and taking the root "-α-" and making it "-ι-" in the optative.
| Past optative | Past potential | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | ||||
| singular | 1st | λόύτιόν | λόύτιόκεν | singular | 1st | λόύτιενεν | λόύτιενκεν |
| 2nd | λόύτιότ | λόύτιόκετ | 2nd | λόύτιενετ | λόύτιενκετ | ||
| 3rd | λόύτιό | λόύτιόκε | 3rd | λόύτιενε | λόύτιενκε | ||
| plural | 1st | λόύτιόνά | λόύτιόκενά | plural | 1st | λόύτιενενά | λόύτιενκενά |
| 2nd | λόύτιότά | λόύτιόκετά | 2nd | λόύτιενετά | λόύτιενκετά | ||
| 3rd | λόύτιόά | λόύτιόκεά | 3rd | λόύτιενεά | λόύτιενκεά | ||
| Passive | λόύτιόκόεν | λόύτιόγ | Passive | λόύτιενεεν | λόύτιενγ | ||