User:Masako/pataka: Difference between revisions
m (→wa) |
|||
| (69 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Help:Wikitext | |||
= Heading 1 = | |||
| | |||
* In syllable codas, {{IPA|[ʃ]}} replaces {{IPA|[s]}}. | |||
* In syllable codas, {{IPA|[ʒ]}} replaces {{IPA|[z]}}. | |||
* {{IPA|[β]}} and {{IPA|[ʙ]}} are in free variation. | |||
* {{IPA|[ʁ]}} and {{IPA|[ʀ]}} are in free variation. | |||
Because of its small phoneme inventory, '''Miyu''' allows for extensive allophonic variation. For example, /p t k/ may be pronounced [b d ɡ] as well as [p t k], /s/ as [z] or [ʃ] as well as [s], /l/ as [ɾ] as well as [l], and vowels may be either long or short. | |||
| | |||
== Heading 2 == | |||
=== Heading 3 === | |||
==== Heading 4 ==== | |||
<nowiki> | |||
{{col-begin}} | |||
{{col-break}} | |||
words | |||
{{col-break}} | |||
| | ety | ||
| | {{col-break}} | ||
| | |||
| | abbs | ||
| | |||
| | {{col-end}} | ||
| | |||
</nowiki> | |||
===== Heading 5 ===== | |||
====== Heading 6 ====== | |||
: = indentation | |||
* Item1 | |||
* Item4 | |||
** Sub-item 4 a) | |||
*** Sub-item 4 a) 1. | |||
**** Sub-item 4 a) 1. i) | |||
** Sub-item 4 b) | |||
* Item5 | |||
# Item1 | |||
# Item4 | |||
## Sub-item 1 | |||
### Sub-sub-item | |||
#### Sub-sub-sub-item | |||
## Sub-item 2 | |||
# Item5 | |||
; Term : Definition1 | |||
; Term | |||
: Definition1 | |||
: Definition2 | |||
: Definition3 | |||
To ''italicize text'', put two consecutive apostrophes on each side of it. | |||
Three apostrophes each side will '''bold the text'''. | |||
Five consecutive apostrophes on each side (two for italics plus three for bold) produces '''''bold italics'''''. | |||
'''''Italic and bold formatting''''' works correctly only within a single line. | |||
For text as {{smallcaps|small caps}}, use the template {{tl|smallcaps}}. | |||
* [[WP:Lingua Franca Nova|LFN]] | |||
* [[Wiktionary:亡|tokomo]] | |||
= old / wrong = | |||
'''Kalo''' is intended to be a minimalist [[wp:Artistic_language|artlang]], not an [[wp:International_auxiliary_language|auxlang]]. It draws primarily on vocabulary from the five most spoken languages in the world; [[wp:List_of_languages_by_number_of_native_speakers|Mandarin, Spanish, English, and Arabic]] ('''Hindi''' is used sparingly although it is spoken by more speakers than Arabic). The grammar is mostly isolating with very few elements of inflection, mostly to show plurality or possession. | |||
'''Kalo''' is NOT meant to mimic, replace, or be inspired by Toki Pona or any [[wp:International_auxiliary_language|IAL]]. Any similarities are based on design aesthetic coincidences and the minimalist nature of the language. | |||
Voiced plosives and affricates, and /f/ occur only in the Southern Tujia dialects. | |||
[n] and [l] are in free variation. | |||
[ɲ] is an allophone of /n/. | |||
/x/ has allophones [ç] before /i/ and [ɸ] before /u/. | |||
=== writing === | |||
[[File:Kaloji.png|thumb|alt=All of the Kalo syllables in Hangul|right|upright=0.75|Kalo Hangul]] | |||
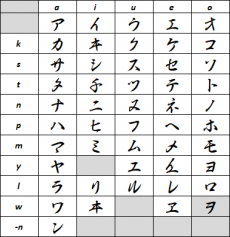
[[File:Kaloji2.png|thumb|alt=A katakana method for writing Kalo|right|upright=0.75|Kalo Katakana]] | |||
== allophony == | |||
The nasal at the end of a syllable can be pronounced as any nasal stop, though it is normally assimilated to the following consonant. That is, it typically occurs as an [n] before /t/ or /s/, as an [m] before /p/, as an [ŋ] before /k/, and as an [ɲ] before /j/. Because of its small phoneme inventory, '''kalo''' allows for quite a lot of allophonic variation. For example, /p t k/ may be pronounced [b d ɡ] as well as [p t k], /s/ as [z] or [ʃ] as well as [s], /l/ as [ɾ] as well as [l], and vowels may be either long or short. Both its sound inventory and phonotactics (patterns of possible sound combinations) are found in the majority of human languages and are therefore readily accessible. | |||
= Syntax = | |||
* '''wa kome''' - <small>1S eat</small> - ''I eat.'' (SV) | |||
: | |||
* '''wa amo ko''' - <small>1S love 3S</small> - ''I love her.'' (SVO) | |||
: | |||
* '''o mala amo''' - <small>DO woman love</small> - ''The woman is loved.'' (OV) | |||
= Nouns = | |||
Nouns only decline for number and possession. They are altered with '''-lo''' to show plurality, and possessiveness with '''-yo'''. | |||
== pronouns == | |||
'''kalo''' has three basic pronouns; '''wa''' [1sg], '''ni''' [2sg], and '''ko''' [3sg]. These do not indicate gender. These can be made plural using the suffix "'''-lo'''", and possessive with "'''-yo'''". | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center; width: 500px;" | |||
== | |||
! | ! | ||
! | ! singular | ||
! | ! plural | ||
! possessive | |||
|-align=center | |-align=center | ||
!''' | ! 1st person | ||
| | | '''wa'''<br>I; me | ||
| '''walo'''<br>we; us | |||
| '''wayo'''<br>my; mine; our(s) | |||
|-align=center | |-align=center | ||
!''' | ! 2nd person | ||
| | | '''ni'''<br>you | ||
| '''nilo'''<br>you (all) | |||
| '''niyo'''<br>your(s) | |||
|-align=center | |-align=center | ||
!''' | ! 3rd person | ||
| | | '''ko'''<br>he; she; him; her; it | ||
| '''kolo'''<br>they; them; those | |||
| '''koyo'''<br>their(s) | |||
|} | |} | ||
''' | * '''walo wite ni''' - <small>1pl see 2s</small> - ''We see you.'' | ||
* '''kolo ne kono wa''' - <small>3pl NEG know 1s</small> - ''They don't know me.'' | |||
== | = Verbs = | ||
Verbs do not change and are only ever modified by particles. | |||
* '''maka''' - do; make; cause (from [[wiktionary:make|make]]) | |||
* '''yo''' - possess; have; hold (from [[wiktionary:有#Definitions|有]]) | |||
== tense, aspect, and mood == | |||
Past tense is indicated by the particle '''le''' ([[wiktionary:了|了]]) following the verb. Future tense is indicated by the particle '''sa''' ([[wiktionary:س#Etymology_2|سَـ]]). | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center; width: 400px;" | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: | |-− | ||
!tense/mood !! particle !! example !! translation | |||
|- | |||
! | |||
! | |||
! | |||
! | |||
! | |||
! | |||
! | |||
|- | |- | ||
|present || - || '''wa ila''' || ''I go'' | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|past || '''le''' || '''wa ila le''' || ''I went'' | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|future || '''sa''' || '''wa ila sa''' || ''I will go'' | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|conditional || '''kisa''' || '''wa ila kisa''' || ''I would go'' | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
<small> | * '''ko ne kome le''' - <small>3sg NEG eat PST</small> - ''He didn't eat.'' | ||
* '''walo wite sa ko''' - <small>1pl see FUT 3sg</small> - ''We will see her.'' | |||
== positional verbs == | |||
'''Kalo''' does not use prepositions, but instead uses positional verbs as auxiliaries. These are also used as temporal adverbs in certain situations. | |||
* '''yu''' - in; at; within; inside; during; between | from ([[wiktionary:于|于]]) | |||
* '''ila''' - be toward; at; in the direction of; go; walk; travel | from ([[wiktionary:إلى|إلى]]) | |||
= Particles = | |||
== determiners == | |||
Determiners in '''kalo''' precede the noun they modify. | |||
=== deixis === | |||
* '''pu''' - this; these | |||
* '''su''' - that; those | |||
=== amount === | |||
* '''aku''' - many; much (one hundred) | |||
* '''kula''' - all; every; each | |||
* '''ne''' - no; none; zero | |||
* '''poka''' - some; several; a few | |||
:: | |||
* '''meno''' - less; fewer / few; a little | |||
* '''maso''' - more | |||
=== other-ness === | |||
* '''asi''' - such | |||
* '''ayo''' - whichever; whatever | |||
* '''oto''' - other | |||
* '''tonye''' - same | |||
= Number = | |||
When numbers one through ten occur independently, the indicator "'''ke'''" precedes the number. | |||
* '''ko yo le o kasa ke li''' | |||
: <small>3s have PST O house NUM two</small> | |||
: ''She had two houses.'' | |||
* '''wa wite o nano ke si''' | |||
: <small>1s see O man NUM four </small> | |||
: ''I see four men.'' | |||
== Higher Numbers == | |||
* '''yewa''' - 11; eleven | |||
* '''yeli''' - 12; twelve | |||
* '''liye''' - 20; twenty | |||
* '''liyesi''' - 24; twenty-four | |||
* '''kuyeli''' - 112; one-hundred-twelve | |||
* '''sankuweyepen''' - 365; three-hundred-sixty-five | |||
__NOTOC__ | |||
<center> | |||
[[#ka|ka]] [[#sa|sa]] [[#ta|ta]] [[#na|na]] [[#pa|pa]] [[#ma|ma]] [[#ya|ya]] [[#la|la]] [[#wa|wa]] [[#a|a i u e o]] | |||
</center> | |||
= ka = | |||
* '''kisa''' /ˈki.sa/ from SPA [[wiktionary:quizá#Spanish|quizá]] | |||
: ''part'' - perhaps; maybe; if; conditional particle [COND] | |||
* '''kute''' /ˈku.te/ from FRE [[wiktionary:écouter|écouter]] | |||
: ''v'' - listen; hear | |||
* '''kono''' /ˈko.no/ from SPA [[wiktionary:conocer#Spanish|conocer]] | |||
: ''n'' - knowledge; awareness; understanding; recognition | |||
: ''v'' - know; understand; be aware (of); recognize | |||
* '''kome''' /ˈko.me/ from SPA [[wiktionary:comer#Spanish|comer]] | |||
: ''v'' - eat; consume; drink | |||
= sa = | |||
* '''sa''' /sa/ from ARA [[wiktionary:س#Etymology_2|سَـ]] | |||
: ''part'' - future tense particle [FUT] | |||
* '''saka/na''' /ˈsa.ka.na/ from ARA [[wiktionary:سخن|سخن]] | |||
: ''v'' - be hot; be warm; burn | |||
: ''n'' - heat; warmth / fire | |||
* '''sana''' /ˈsa.na/ from ARA [[wiktionary:سنة|سنة]] | |||
: ''n'' - year; 365 days | |||
* '''sapa''' /ˈsa.pa/ from ARA [[wiktionary:سبب|سبب]] | |||
: ''n'' - cause; reason; purpose; rationale; motive | |||
* '''salama''' /sa.ˈla.ma/ from ARA [[wiktionary:سلم#Arabic|سلم]] | |||
: ''n'' - peace; calm; tranquility; quiet | |||
: ''v'' - be peaceful; be calm | |||
: ''intj'' - Peace! Hey! Hi! | |||
* '''sawa''' /ˈsa.wa/ from ARA [[wiktionary:زوج|زوج]] | |||
: ''n'' - spouse; husband; wife; sweetheart; mate | |||
: ''v'' - marry | |||
* '''si''' /si/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:四#Definitions|四]] | |||
: ''num'' - four; 4 | |||
* '''siya''' /ˈsi.ja/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:下#Definitions|下]] | |||
: ''prep'' - below; under; beneath | |||
: ''v'' - be under; be lower | |||
* '''su''' /su/ from TUR [[wiktionary:şu#Turkish|şu]] | |||
: ''part'' - that; those (over there) | |||
* '''sunya''' /ˈsun.ja/ from HIN [[wiktionary:शून्य|शून्य]] | |||
: ''num'' - zero; 0 | |||
: ''n'' - nothing | |||
: ''v'' - be empty; be void | |||
* '''se''' /se/ from SPA [[wiktionary:se#Spanish|se]] | |||
: ''pro'' - reflexive / reciprocal pronoun | |||
* '''sosa''' /ˈso.sa/ from SPA [[wiktionary:salsa#Spanish|salsa]] | |||
: ''n'' - juice; sauce; gravy; dressing | |||
= ta = | |||
* '''tanka''' /ˈtaŋ.ka/ from ENG/GER [[wiktionary:thank|thank]]/[[wiktionary:danke#German|danke]] | |||
: ''v'' - to thank; show appreciation; express gratitude | |||
: ''part/intj'' - thank you; thanks | |||
* '''tapo''' /ˈta.po/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:打破|打破]] | |||
: ''v'' - damage; wreck; break; destroy | |||
: ''n'' - destruction; damage | |||
* '''tipa''' /ˈti.pa/ (or '''tupa''' /ˈtu.pa/) from ARA [[wiktionary:طيب|طيب]] (or [[wiktionary:טוב|טוב]]) | |||
: ''v'' - be good; pleasant; agreeable; nice; sweet; OK | |||
: ''intj'' - great! good! thanks! OK! cool! yay! | |||
* '''tiya''' /ˈti.ja/ from SPA [[wiktionary:tía#Spanish|tía]] | |||
: ''n'' - aunt/uncle; extended family | |||
* '''te''' /te/ from SPA/ZHO [[wiktionary:de#Etymology_2_10|de]]/[[wiktionary:的#Definitions_2|的]] | |||
: ''v'' - to move away from | |||
: ''prep'' - of; from | |||
* '''tenpo''' /ˈtem.po/ from SPA [[wiktionary:tiempo#Spanish|tiempo]] | |||
: ''n'' - time; moment; period | |||
* '''tela''' or '''talo''' /ˈte.la/ or /ˈta.lo/ from ENG [[wiktionary:tell|tell]] | |||
: ''n'' - language; talk; speech | |||
: ''v'' - talk; speak; discuss; say; tell | |||
* '''tonpa''' /ˈtom.pa/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:同胞#Mandarin|同胞]] | |||
: ''n'' - sibling; compatriot; friend | |||
| ''' | |||
| ''' | * '''tonye''' /ˈto.ɲe/ (or '''ton''' /ton/) from ZHO [[wiktionary:同一#Mandarin|同一]] | ||
: ''v'' - be identical; same; equivalent; equal | |||
= na = | |||
* '''nai''' /naɪ/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:內#Japanese|內]] | |||
: ''v'' - be inside; within | |||
: ''prep'' - inside; within; during; while | |||
* '''nano''' /ˈna.no/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:男#Definitions|男]] | |||
: ''n'' - man; male | |||
| ''' | |||
| ''' | * '''nama''' /ˈna.ma/ from ARA [[wiktionary:نام#Verb|نام]] | ||
| ''' | : ''v'' - sleep; rest; relax | ||
| ''' | * '''naya''' /ˈna.ja/ from HIN [[wiktionary:नया|नया]] | ||
: ''v'' - be new; fresh; young | |||
| ''' | |||
* '''nalu''' /ˈna.lu/ from JPN [[wiktionary:なる|なる]] | |||
: ''v'' - succeed; finish; complete; accomplish; become; turn into | |||
* '''ni''' /ni/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:你#Definitions|你]] | |||
| | : ''pro'' - you [2sg] | ||
* '''nun''' /nun/ from PIE [[wiktionary:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₁néwn̥|h₁néwn̥]] | |||
: ''num'' - nine; 9 | |||
* '''ne''' /ne/ from ENG [[wiktionary:nay#Interjection|nay]] | |||
: ''part'' - no; not; negative [NEG] | |||
* '''nesi''' /ˈne.si/ from SPA [[wiktionary:necesitar#Spanish|necesitar]] | |||
: ''v'' - need; require; must | |||
: ''n'' - obligation; need | |||
* '''nen/ka''' /ˈnen.ka/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:能#Definitions|能]] | |||
: ''v'' - be able to; be capable; be possible | |||
: ''n'' - potential; possibility; capability | |||
* '''note''' /ˈno.te/ from SPA [[wiktionary:noche#Spanish|noche]] | |||
: ''n'' - night; darkness | |||
= pa = | |||
* '''pa''' /pa/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:八|八]] | |||
: ''num'' - eight; 8 | |||
* '''pan''' /pan/ from SPA/ZHO [[wiktionary:pan#Spanish|pan]]/[[wiktionary:飯|飯]] | |||
: ''n'' - bread; food; sustenance | |||
* '''pala''' /ˈpa.la/ from SPA [[wiktionary:palabra#Spanish|palabra]] | |||
: ''n'' - word; morpheme; lexeme | |||
* '''pina''' /ˈpi.na/ from ARA [[wiktionary:ابن|ابن]] | |||
: ''n'' - child; offspring; kid | |||
* '''pu''' /pu/ from TUR [[wiktionary:bu#Turkish|bu]] | |||
: ''part'' - this; these (here) | |||
* '''pula''' /ˈpu.la/ from HIN [[wiktionary:बुरा|बुरा]] | |||
: ''n'' - evil | |||
: ''v'' - be bad; spoiled; be broken; to break down; be wicked; be evil | |||
* '''pen''' /pen/ from ELL [[wiktionary:πέντε#Greek|πέντε]] | |||
: ''num'' - five; 5 | |||
* '''po''' /po/ from SPA [[wiktionary:por#Spanish|por]] | |||
: ''prep'' - by; for; [be] about | |||
: ''v'' - [go] through; [move] across | |||
* '''poka''' /ˈpo.ka/ from SPA [[wiktionary:poco#Spanish|poca]] | |||
: ''v'' - be small; little | |||
: ''v'' - be few; less | |||
* '''ponte''' /ˈpon.te/ from ENG [[wiktionary:ponder|ponder]] | |||
: ''v'' - think; ponder; consider; weigh | |||
: ''n'' - thought; idea; consideration | |||
* '''pone''' /ˈpo.ne/ from SPA [[wiktionary:poner|poner]] | |||
: ''v'' - to put, to place, to set | |||
= ma = | |||
* '''ma''' /ma/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:嗎#Chinese|嗎]] | |||
: ''part'' - interrogative particle [Q] | |||
* '''maka''' /ˈma.ka/ from ENG [[wiktionary:make|make]] | |||
: ''n'' - cause; action; happening | |||
: ''v'' - do; make; cause; happen | |||
* '''maso''' /ˈma.so/ from SPA [[wiktionary:más#Spanish|más]] | |||
[[ | : ''part'' - more; again | ||
: ''n'' - layer; repetition; addition | |||
: ''v'' - add; repeat; layer | |||
* ''' | * '''mala''' /ˈma.la/ from ARA [[wiktionary:امرأة|امرأة]] | ||
: ''n'' - woman; female; wife | |||
* '''mila''' /ˈmi.la/ from SPA [[wiktionary:mil#Spanish|mil]] | |||
: ''num'' - thousand; 1000 | |||
* '''muki''' /ˈmu.ki/ from ARA [[wiktionary:مهم|مهم]] | |||
: ''n'' - importance; significance | |||
: ''v'' - be important; matter | |||
* '''muna''' /ˈmu.na/ from ENG [[wiktionary:moon#English|moon]] | |||
: ''n'' - moon; month | |||
* '''me''' /me/ from FRE [[wiktionary:mais#French|mais]] | |||
: ''part'' - but; however; although | |||
* '''moto''' /ˈmo.to/ from SPA [[wiktionary:modo#Spanish|modo]] | |||
: ''n'' - mood; manner; way; method | |||
= ya = | |||
* '''ya''' /ja/ from ARA [[wiktionary:يا#Arabic|يا]] | |||
: ''part'' - vocative marker [VOC]; hey; let's ~ | |||
* '''yati''' /ˈja.ti/ from ARA [[wiktionary:يد|يد]] | |||
: ''n'' - hand; arm | |||
: ''v'' - give; transfer | |||
* '''yapu''' /ˈja.pu/ from ARA [[wiktionary:عفا|عفا]] | |||
: ''n'' - pardon; excuse; forgiveness | |||
: ''v'' - pardon; excuse; forgive | |||
* '''yame''' /ˈja.me/ from ARA [[wiktionary:جمع|جمع]] | |||
: ''n'' - collection; gathering; group; set | |||
: ''v'' - gather; collect; assemble; unite | |||
* ''' | * '''yu''' /ju/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:於#Definitions|于]] | ||
: ''v'' - be in; at; out of | |||
: ''prep'' - in; at; to; by; than; out of | |||
* '''yuma''' /ˈju.ma/ from ARA [[wiktionary:يوم#Arabic|يوم]] | |||
: ''n'' - day; daylight; 24 hour period | |||
* | * '''ye''' /je/ from KOR [[wiktionary:열#Korean|열]] | ||
: ''num'' - ten; 10 | |||
: | |||
: | |||
* '''yeko''' /ˈje.ko/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:以後#Chinese|以后]] | |||
: ''prep'' - back; behind; rear; afterwards; after; later | |||
: ''adv'' - from now on; henceforth | |||
* '''yo''' /jo/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:有#Definitions|有]] | |||
: ''v'' - have; possess; carry; hold; keep | |||
= la = | |||
* '''laka''' /ˈla.ka/ from ARA [[wiktionary:رقم|رقم]] | |||
: ''n'' - number; digit; amount | |||
: ''v'' - count; enumerate | |||
* '''lata''' /ˈla.ta/ from SPA [[wiktionary:lata#Spanish|lata]] | |||
: ''n'' - box; bucket; basket; container; vessel | |||
: ''v'' - carry; tote; transport | |||
* '''li''' /li/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:兩#Definitions|兩]] | |||
: ''num'' - two; double; duo | |||
: ''pro'' - some; a few | |||
* '''le''' /le/ from ZHO [[wiktionary:了|了]] | |||
: ''part'' - past tense marker [PST] | |||
| | |||
* '''loka''' /ˈlo.ka/ from SPA [[wiktionary:local#Spanish|local]] | |||
: ''n'' - place; location; point; spot | |||
= wa = | |||
* '''wa''' /wa/ from ARA/ZHO [[wiktionary:واحد|واحد]]/[[wiktionary:我|我]] | |||
: ''pro'' - I; me [1sg] | |||
: ''num'' - one; 1; single | |||
: ''v'' - be alone; be singular | |||
* | * '''waya''' /ˈwa.ja/ from HIN [[wiktionary:वयस्क|वयस्क]] | ||
: ''v'' - grow; mature; develop | |||
: ''n'' - adult; mature thing | |||
* '''wino''' /ˈwi.no/ from SPA [[wiktionary:vino#Spanish|vino]] | |||
: ''n'' - alcohol; beer; wine | |||
: ''v'' - drink ~ | |||
* '''we''' /we/ from PIE [[wiktionary:econstruction:Proto-Indo-European/swéḱs|swéḱs]] | |||
: ''num'' - six; 6 | |||
* | * '''weko''' /ˈwe.ko/ from SPA [[wiktionary:hueco|hueco]] | ||
: ''n'' - door, hole, orifice, window; port | |||
* '''wento''' /ˈwen.to/ from SPA [[wiktionary:viento|viento]] | |||
: ''n'' - air; wind; void; essence; spirit | |||
''' | * '''wela''' /ˈwe.la/ from SPA [[wiktionary:fuera#Spanish|fuera]] | ||
: ''prep'' - outside; exterior | |||
: ''v'' - leave; exit | |||
= a = | |||
* '''alima''' /a.ˈli.ma/ from ARA [[wiktionary:علم|علم]] | |||
: ''v'' - to discern, to find out, to learn | |||
: ''n'' - learning; education; knowledge | |||
* '''amo''' /ˈa.mo/ from SPA [[wiktionary:amor#Spanish|amor]] | |||
: ''n'' - love; affection; adoration | |||
: ''v'' - love; adore; like | |||
* '''ante''' /ˈan.te/ from SPA [[wiktionary:ante#Spanish|ante]] | |||
: ''n'' - front side; chest; fore area | |||
: ''prep'' - before; in front; forward; ahead | |||
* '''asi''' /ˈa.si/ from SPA [[wiktionary:así#Spanish|así]] | |||
: ''part'' - like this/that; as [such]; thus; so | |||
* ''' | |||
: '' | |||
* ''' | * '''awa''' /ˈa.wa/ from ARA [[wiktionary:أو|أو]] | ||
: ''part'' - either; or; other | |||
: '' | |||
* ''' | * '''ayo''' /ˈa.jo/ from ARA [[wiktionary:أي|أي]] | ||
:''part'' - whichever; whatever; something [INDEF] | |||
: '' | |||
* '''e''' /e/ from SPA/ZHO [[wiktionary:e#Etymology_2_17|e]]/[[wiktionary:和#Definitions_2|和]] | |||
: ''part'' - and; also; too | |||
* '''ila''' /ˈi.la/ from ARA [[wiktionary:إلى|إلى]] | |||
: ''prep'' - toward; at; in direction of | |||
: ''v'' - go (toward); walk; travel | |||
: '' | |||
* ''' | * '''o''' /o/ from JPN [[wiktionary:を#Etymology_2|を]] | ||
: | : ''part'' - direct object particle | ||
: '' | |||
* wikitravel.org/en/Spanish_phrasebook | |||
* en.wiktionary.org/wiki/Category:Phrasebooks_by_language | |||
A working phrasebook for [[Kalo]]. | |||
= Essentials = | |||
* '''ola''' - Used for "hello; goodbye; farewell; welcome" (analogous to [[wiktionary:aloha#Hawaiian|aloha]]) | |||
* ''' | * '''kan/a''' - "yes; it is" | ||
* '''ne''' - "no; it is not" | |||
* ''' | |||
* '''yapu wa''' - "Excuse me." | |||
* '''nenka ma''' - "Please." [''lit'': is (it) possible?] | |||
:: by extension "Do you mind?" | |||
* '''tanka (ta)''' - "Thank you (very much)." | |||
* '''tipa''' - "(That's) OK." | |||
= Greetings & Goodbyes = | |||
* '''ola yuma''' - "Good morning/day/afternoon" | |||
* '''ola note''' - "Good evening/night" | |||
* '''salama''' - "Hey/Hi/Hello/Bye" | |||
== | == Civilities == | ||
* '''moto (niyo) ma''' - <small>manner 2s.POSS Q</small> - ''How are you?'' | |||
** '''tipa''' - "Good/OK/Fine." | |||
** '''...''' - "Not bad." | |||
* '''tenpo ta ne wite''' - <small>time big no see</small> - ''Long time no see'' | |||
Latest revision as of 10:48, 8 April 2025
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Help:Wikitext
Heading 1
- In syllable codas, [ʃ] replaces [s].
- In syllable codas, [ʒ] replaces [z].
- [β] and [ʙ] are in free variation.
- [ʁ] and [ʀ] are in free variation.
Because of its small phoneme inventory, Miyu allows for extensive allophonic variation. For example, /p t k/ may be pronounced [b d ɡ] as well as [p t k], /s/ as [z] or [ʃ] as well as [s], /l/ as [ɾ] as well as [l], and vowels may be either long or short.
Heading 2
Heading 3
Heading 4
{{col-begin}} {{col-break}} words {{col-break}} ety {{col-break}} abbs {{col-end}}
Heading 5
Heading 6
- = indentation
- Item1
- Item4
- Sub-item 4 a)
- Sub-item 4 a) 1.
- Sub-item 4 a) 1. i)
- Sub-item 4 a) 1.
- Sub-item 4 b)
- Sub-item 4 a)
- Item5
- Item1
- Item4
- Sub-item 1
- Sub-sub-item
- Sub-sub-sub-item
- Sub-sub-item
- Sub-item 2
- Sub-item 1
- Item5
- Term
- Definition1
- Term
- Definition1
- Definition2
- Definition3
To italicize text, put two consecutive apostrophes on each side of it.
Three apostrophes each side will bold the text.
Five consecutive apostrophes on each side (two for italics plus three for bold) produces bold italics.
Italic and bold formatting works correctly only within a single line.
For text as Template:Smallcaps, use the template {{smallcaps}}.
old / wrong
Kalo is intended to be a minimalist artlang, not an auxlang. It draws primarily on vocabulary from the five most spoken languages in the world; Mandarin, Spanish, English, and Arabic (Hindi is used sparingly although it is spoken by more speakers than Arabic). The grammar is mostly isolating with very few elements of inflection, mostly to show plurality or possession.
Kalo is NOT meant to mimic, replace, or be inspired by Toki Pona or any IAL. Any similarities are based on design aesthetic coincidences and the minimalist nature of the language.
Voiced plosives and affricates, and /f/ occur only in the Southern Tujia dialects. [n] and [l] are in free variation. [ɲ] is an allophone of /n/. /x/ has allophones [ç] before /i/ and [ɸ] before /u/.
writing
allophony
The nasal at the end of a syllable can be pronounced as any nasal stop, though it is normally assimilated to the following consonant. That is, it typically occurs as an [n] before /t/ or /s/, as an [m] before /p/, as an [ŋ] before /k/, and as an [ɲ] before /j/. Because of its small phoneme inventory, kalo allows for quite a lot of allophonic variation. For example, /p t k/ may be pronounced [b d ɡ] as well as [p t k], /s/ as [z] or [ʃ] as well as [s], /l/ as [ɾ] as well as [l], and vowels may be either long or short. Both its sound inventory and phonotactics (patterns of possible sound combinations) are found in the majority of human languages and are therefore readily accessible.
Syntax
- wa kome - 1S eat - I eat. (SV)
- wa amo ko - 1S love 3S - I love her. (SVO)
- o mala amo - DO woman love - The woman is loved. (OV)
Nouns
Nouns only decline for number and possession. They are altered with -lo to show plurality, and possessiveness with -yo.
pronouns
kalo has three basic pronouns; wa [1sg], ni [2sg], and ko [3sg]. These do not indicate gender. These can be made plural using the suffix "-lo", and possessive with "-yo".
| singular | plural | possessive | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st person | wa I; me |
walo we; us |
wayo my; mine; our(s) |
| 2nd person | ni you |
nilo you (all) |
niyo your(s) |
| 3rd person | ko he; she; him; her; it |
kolo they; them; those |
koyo their(s) |
- walo wite ni - 1pl see 2s - We see you.
- kolo ne kono wa - 3pl NEG know 1s - They don't know me.
Verbs
Verbs do not change and are only ever modified by particles.
tense, aspect, and mood
Past tense is indicated by the particle le (了) following the verb. Future tense is indicated by the particle sa (سَـ).
| tense/mood | particle | example | translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| present | - | wa ila | I go |
| past | le | wa ila le | I went |
| future | sa | wa ila sa | I will go |
| conditional | kisa | wa ila kisa | I would go |
- ko ne kome le - 3sg NEG eat PST - He didn't eat.
- walo wite sa ko - 1pl see FUT 3sg - We will see her.
positional verbs
Kalo does not use prepositions, but instead uses positional verbs as auxiliaries. These are also used as temporal adverbs in certain situations.
- yu - in; at; within; inside; during; between | from (于)
- ila - be toward; at; in the direction of; go; walk; travel | from (إلى)
Particles
determiners
Determiners in kalo precede the noun they modify.
deixis
- pu - this; these
- su - that; those
amount
- aku - many; much (one hundred)
- kula - all; every; each
- ne - no; none; zero
- poka - some; several; a few
- meno - less; fewer / few; a little
- maso - more
other-ness
- asi - such
- ayo - whichever; whatever
- oto - other
- tonye - same
Number
When numbers one through ten occur independently, the indicator "ke" precedes the number.
- ko yo le o kasa ke li
- 3s have PST O house NUM two
- She had two houses.
- wa wite o nano ke si
- 1s see O man NUM four
- I see four men.
Higher Numbers
- yewa - 11; eleven
- yeli - 12; twelve
- liye - 20; twenty
- liyesi - 24; twenty-four
- kuyeli - 112; one-hundred-twelve
- sankuweyepen - 365; three-hundred-sixty-five
ka
- kisa /ˈki.sa/ from SPA quizá
- part - perhaps; maybe; if; conditional particle [COND]
- kute /ˈku.te/ from FRE écouter
- v - listen; hear
- kono /ˈko.no/ from SPA conocer
- n - knowledge; awareness; understanding; recognition
- v - know; understand; be aware (of); recognize
- kome /ˈko.me/ from SPA comer
- v - eat; consume; drink
sa
- sa /sa/ from ARA سَـ
- part - future tense particle [FUT]
- saka/na /ˈsa.ka.na/ from ARA سخن
- v - be hot; be warm; burn
- n - heat; warmth / fire
- sana /ˈsa.na/ from ARA سنة
- n - year; 365 days
- sapa /ˈsa.pa/ from ARA سبب
- n - cause; reason; purpose; rationale; motive
- salama /sa.ˈla.ma/ from ARA سلم
- n - peace; calm; tranquility; quiet
- v - be peaceful; be calm
- intj - Peace! Hey! Hi!
- sawa /ˈsa.wa/ from ARA زوج
- n - spouse; husband; wife; sweetheart; mate
- v - marry
- si /si/ from ZHO 四
- num - four; 4
- siya /ˈsi.ja/ from ZHO 下
- prep - below; under; beneath
- v - be under; be lower
- su /su/ from TUR şu
- part - that; those (over there)
- sunya /ˈsun.ja/ from HIN शून्य
- num - zero; 0
- n - nothing
- v - be empty; be void
- se /se/ from SPA se
- pro - reflexive / reciprocal pronoun
- sosa /ˈso.sa/ from SPA salsa
- n - juice; sauce; gravy; dressing
ta
- v - to thank; show appreciation; express gratitude
- part/intj - thank you; thanks
- tapo /ˈta.po/ from ZHO 打破
- v - damage; wreck; break; destroy
- n - destruction; damage
- v - be good; pleasant; agreeable; nice; sweet; OK
- intj - great! good! thanks! OK! cool! yay!
- tiya /ˈti.ja/ from SPA tía
- n - aunt/uncle; extended family
- v - to move away from
- prep - of; from
- tenpo /ˈtem.po/ from SPA tiempo
- n - time; moment; period
- tela or talo /ˈte.la/ or /ˈta.lo/ from ENG tell
- n - language; talk; speech
- v - talk; speak; discuss; say; tell
- tonpa /ˈtom.pa/ from ZHO 同胞
- n - sibling; compatriot; friend
- tonye /ˈto.ɲe/ (or ton /ton/) from ZHO 同一
- v - be identical; same; equivalent; equal
na
- nai /naɪ/ from ZHO 內
- v - be inside; within
- prep - inside; within; during; while
- nano /ˈna.no/ from ZHO 男
- n - man; male
- nama /ˈna.ma/ from ARA نام
- v - sleep; rest; relax
- naya /ˈna.ja/ from HIN नया
- v - be new; fresh; young
- nalu /ˈna.lu/ from JPN なる
- v - succeed; finish; complete; accomplish; become; turn into
- ni /ni/ from ZHO 你
- pro - you [2sg]
- nun /nun/ from PIE h₁néwn̥
- num - nine; 9
- ne /ne/ from ENG nay
- part - no; not; negative [NEG]
- nesi /ˈne.si/ from SPA necesitar
- v - need; require; must
- n - obligation; need
- nen/ka /ˈnen.ka/ from ZHO 能
- v - be able to; be capable; be possible
- n - potential; possibility; capability
- note /ˈno.te/ from SPA noche
- n - night; darkness
pa
- pa /pa/ from ZHO 八
- num - eight; 8
- n - bread; food; sustenance
- pala /ˈpa.la/ from SPA palabra
- n - word; morpheme; lexeme
- pina /ˈpi.na/ from ARA ابن
- n - child; offspring; kid
- pu /pu/ from TUR bu
- part - this; these (here)
- pula /ˈpu.la/ from HIN बुरा
- n - evil
- v - be bad; spoiled; be broken; to break down; be wicked; be evil
- pen /pen/ from ELL πέντε
- num - five; 5
- po /po/ from SPA por
- prep - by; for; [be] about
- v - [go] through; [move] across
- poka /ˈpo.ka/ from SPA poca
- v - be small; little
- v - be few; less
- ponte /ˈpon.te/ from ENG ponder
- v - think; ponder; consider; weigh
- n - thought; idea; consideration
- pone /ˈpo.ne/ from SPA poner
- v - to put, to place, to set
ma
- ma /ma/ from ZHO 嗎
- part - interrogative particle [Q]
- maka /ˈma.ka/ from ENG make
- n - cause; action; happening
- v - do; make; cause; happen
- maso /ˈma.so/ from SPA más
- part - more; again
- n - layer; repetition; addition
- v - add; repeat; layer
- mala /ˈma.la/ from ARA امرأة
- n - woman; female; wife
- mila /ˈmi.la/ from SPA mil
- num - thousand; 1000
- muki /ˈmu.ki/ from ARA مهم
- n - importance; significance
- v - be important; matter
- muna /ˈmu.na/ from ENG moon
- n - moon; month
- me /me/ from FRE mais
- part - but; however; although
- moto /ˈmo.to/ from SPA modo
- n - mood; manner; way; method
ya
- ya /ja/ from ARA يا
- part - vocative marker [VOC]; hey; let's ~
- yati /ˈja.ti/ from ARA يد
- n - hand; arm
- v - give; transfer
- yapu /ˈja.pu/ from ARA عفا
- n - pardon; excuse; forgiveness
- v - pardon; excuse; forgive
- yame /ˈja.me/ from ARA جمع
- n - collection; gathering; group; set
- v - gather; collect; assemble; unite
- yu /ju/ from ZHO 于
- v - be in; at; out of
- prep - in; at; to; by; than; out of
- yuma /ˈju.ma/ from ARA يوم
- n - day; daylight; 24 hour period
- ye /je/ from KOR 열
- num - ten; 10
- yeko /ˈje.ko/ from ZHO 以后
- prep - back; behind; rear; afterwards; after; later
- adv - from now on; henceforth
- yo /jo/ from ZHO 有
- v - have; possess; carry; hold; keep
la
- laka /ˈla.ka/ from ARA رقم
- n - number; digit; amount
- v - count; enumerate
- lata /ˈla.ta/ from SPA lata
- n - box; bucket; basket; container; vessel
- v - carry; tote; transport
- li /li/ from ZHO 兩
- num - two; double; duo
- pro - some; a few
- le /le/ from ZHO 了
- part - past tense marker [PST]
- loka /ˈlo.ka/ from SPA local
- n - place; location; point; spot
wa
- pro - I; me [1sg]
- num - one; 1; single
- v - be alone; be singular
- waya /ˈwa.ja/ from HIN वयस्क
- v - grow; mature; develop
- n - adult; mature thing
- wino /ˈwi.no/ from SPA vino
- n - alcohol; beer; wine
- v - drink ~
- we /we/ from PIE swéḱs
- num - six; 6
- weko /ˈwe.ko/ from SPA hueco
- n - door, hole, orifice, window; port
- wento /ˈwen.to/ from SPA viento
- n - air; wind; void; essence; spirit
- wela /ˈwe.la/ from SPA fuera
- prep - outside; exterior
- v - leave; exit
a
- alima /a.ˈli.ma/ from ARA علم
- v - to discern, to find out, to learn
- n - learning; education; knowledge
- amo /ˈa.mo/ from SPA amor
- n - love; affection; adoration
- v - love; adore; like
- ante /ˈan.te/ from SPA ante
- n - front side; chest; fore area
- prep - before; in front; forward; ahead
- asi /ˈa.si/ from SPA así
- part - like this/that; as [such]; thus; so
- awa /ˈa.wa/ from ARA أو
- part - either; or; other
- ayo /ˈa.jo/ from ARA أي
- part - whichever; whatever; something [INDEF]
- part - and; also; too
- ila /ˈi.la/ from ARA إلى
- prep - toward; at; in direction of
- v - go (toward); walk; travel
- o /o/ from JPN を
- part - direct object particle
- wikitravel.org/en/Spanish_phrasebook
- en.wiktionary.org/wiki/Category:Phrasebooks_by_language
A working phrasebook for Kalo.
Essentials
- ola - Used for "hello; goodbye; farewell; welcome" (analogous to aloha)
- kan/a - "yes; it is"
- ne - "no; it is not"
- yapu wa - "Excuse me."
- nenka ma - "Please." [lit: is (it) possible?]
- by extension "Do you mind?"
- tanka (ta) - "Thank you (very much)."
- tipa - "(That's) OK."
Greetings & Goodbyes
- ola yuma - "Good morning/day/afternoon"
- ola note - "Good evening/night"
- salama - "Hey/Hi/Hello/Bye"
Civilities
- moto (niyo) ma - manner 2s.POSS Q - How are you?
- tipa - "Good/OK/Fine."
- ... - "Not bad."
- tenpo ta ne wite - time big no see - Long time no see